Michaelis Menten Vs Lineweaver Burk
Tumor M2-PK is a synonym for the dimeric grade of the pyruvate kinase isoenzyme blazon M2 (PKM2), a cardinal enzyme within tumor metabolism. Tumor M2-PK can exist elevated in many tumor types, rather than beingness an organ-specific tumor marker such equally PSA. Increased stool (fecal) levels are being investigated as a method of screening for colorectal tumors, and EDTA plasma levels are undergoing testing for possible application in the follow-up of various cancers.
Sandwich ELISAs based on ii monoclonal antibodies which specifically recognize Tumor M2-PK (the dimeric form of M2-PK) are bachelor for the quantification of Tumor M2-PK in stool and EDTA-plasma samples respectively. As a biomarker, the amount of Tumor M2-PK in stool and EDTA-plasma reflects the specific metabolic condition of the tumors.
Early detection of colorectal tumors and polyps [edit]
M2-PK, as measured in feces, is a potential tumor marker for colorectal cancer. When measured in feces with a cutoff value of 4 U/ml, its sensitivity has been estimated to be 85% (with a 95% confidence interval of 65 to 96%) for colon cancer and 56% (confidence interval 41–74%) for rectal cancer.[1] Its specificity is 95%.[2]
The M2-PK examination is not dependent on occult blood (ELISA method), so it can detect bleeding or non-bleeding bowel cancer and besides polyps with high sensitivity and high specificity with no false negative, just false positives may occur.[three]
Most people are more willing to accept non-invasive preventive medical check-ups. Therefore, the measurement of tumor M2-PK in stool samples, with follow-up by colonoscopy to clarify the tumor M2-PK positive results, may show to exist an accelerate in the early on detection of colorectal carcinomas. The CE marked M2-PK Test is available in form of an ELISA test for quantitative results or as point of intendance exam to receive results inside minutes.
Tumor M2-PK is also useful to diagnose lung cancer and amend than SCC and NSE tumor markers.[four] With renal prison cell carcinoma (RCC), the M2PK exam has sensitivity of 66.vii percent for metastatic RCC and 27.5 percentage for nonmetastatic RCC, but M2PK exam cannot detect transitional cell carcinoma of the float, prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia.[five]
Cancer follow-upward [edit]
Studies from various international working groups take revealed a significantly increased corporeality of Tumor M2-PK in EDTA-plasma samples of patients with renal, lung, breast, cervical and gastrointestinal tumors (oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, colon, rectum), equally well as melanoma, which correlated with the tumor stage.
The combination of Tumor M2-PK with the appropriate classical tumor marker, such as CEA for bowel cancer, CA 19-9 for pancreatic cancer and CA 72-4 for gastric cancer, significantly increases the sensitivity to observe various cancers.
An important application of the Tumor M2-PK examination in EDTA-plasma is for follow-upwards during tumor therapy, to monitor the success or failure of the chosen handling, besides equally predicting the chances of a "cure" and survival.
If Tumor M2-PK levels subtract during therapy and and so remain low later on therapy it points towards successful treatment. An increment in the Tumor M2-PK values during or after therapy points towards relapse and/or metastasis.
Increased Tumor M2-PK values tin can sometimes as well occur in severe inflammatory diseases, which must be excluded by differential diagnosis.
Tetrameric and dimeric PKM2 [edit]
Pyruvate kinase catalyzes the terminal step within the glycolytic sequence, the dephosphorylation of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate and is responsible for internet energy production within the glycolytic pathway. Depending upon the different metabolic functions of the tissues, different isoenzymes of pyruvate kinase are expressed.
M2-PK (PKM2) is the predominant pyruvate kinase isoform in proliferating cells, such as fibroblasts, embryonic cells and adult stem cells and most human tissue, including lung, bladder, kidney and thymus; M2-PK is upgregulated in many human being tumors.[6]
M2-PK can occur in 2 different forms in proliferating cells:
- a tetrameric form, which consists of 4 subunits
- a dimeric class, consisting of 2 subunits.
The tetrameric form of M2-PK has a high affinity to its substrate, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), and is highly active at physiological PEP concentrations. Furthermore, the tetrameric form of M2-PK is associated with several other glycolytic enzymes inside the then-chosen glycolytic enzyme complex. Due to the close proximity of the enzymes, the association within the glycolytic enzyme complex leads to a highly effective conversion of glucose to lactate. When M2-PK is mainly in the highly active tetrameric course, which is the instance in well-nigh normal cells, glucose is mostly converted to lactate, with the attendant production of energy.
In contrast, the dimeric form of M2-PK has a depression affinity for phosphoenolpyruvate, being well-nigh inactive at physiological PEP concentrations. When M2-PK is mainly in the dimeric class, which is the instance in tumor cells, all phosphometabolites above pyruvate kinase accumulate and are channelled into synthetic processes which branch off from glycolytic intermediates, such every bit nucleic acids, phospholipids and amino acids, important cell building blocks for highly proliferating cells such as tumor cells.
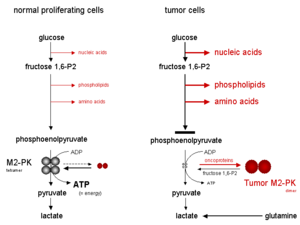
Metabolic consequences of the tetrameric and dimeric forms of M2-PK
As a consequence of the primal position of pyruvate kinase inside glycolysis, the tetramer : dimer ratio of M2-PK determines whether glucose carbons are converted to pyruvate and lactate, along with the production of free energy (tetrameric course), or channelled into constructed processes (dimeric form). In tumor cells M2-PK is mainly in the dimeric form. Therefore, the dimeric form of M2-PK has been termed Tumor M2-PK.
The dimerization of M2-PK in tumor cells is induced past the direct interaction of M2-PK with different oncoproteins.
However, the tetramer : dimer ratio of M2-PK is non abiding.
Oxygen starvation or highly accumulated glycolytic intermediates, such as fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (fructose 1,6-P2) or the amino acid serine, induce the reassociation of the dimeric form of M2-PK to the tetrameric form. Consequently, due to the activation of M2-PK, glucose is converted to pyruvate and lactate under the production of energy until the fructose ane,half-dozen-P2 levels drop below a sure threshold value, which allows the dissociation of the tetrameric form of M2-PK to the dimeric course. Thereafter, the cycle of oscillation starts over again when the fructose i,half-dozen-P2 levels reach a certain upper threshold value which induces the tetramerization of M2-PK.
When M2-PK is mainly in the less active dimeric class, energy is produced by the degradation of the amino acid glutamine to aspartate, pyruvate and lactate, which is termed glutaminolysis.
In tumor cells the increased rate of lactate production in the presence of oxygen is termed the Warburg effect.
Mutations [edit]
For the get-go fourth dimension pyruvate kinase M2 enzyme was reported with two missense mutations, H391Y and K422R, found in cells from Bloom syndrome patients, decumbent to develop cancer. Results show that despite the presence of mutations in the inter-subunit contact domain, the K422R and H391Y mutant proteins maintained their homotetrameric structure, similar to the wild-type protein, but showed a loss of activeness of 75 and 20%, respectively. H391Y showed a 6-fold increase in affinity for its substrate phosphoenolpyruvate and behaved like a non-allosteric poly peptide with compromised cooperative binding. However, the affinity for phosphoenolpyruvate was lost significantly in K422R. Unlike K422R, H391Y showed enhanced thermal stability, stability over a range of pH values, a lesser consequence of the allosteric inhibitor Phe, and resistance toward structural amending upon binding of the activator (fructose 1,6-bisphosphate) and inhibitor (Phe). Both mutants showed a slight shift in the pH optimum from 7.4 to 7.0.[7] The co-expression of homotetrameric wild type and mutant PKM2 in the cellular milieu resulting in the interaction betwixt the two at the monomer level was substantiated farther by in vitro experiments. The cantankerous-monomer interaction significantly contradistinct the oligomeric country of PKM2 by favoring dimerisation and heterotetramerization. In silico study provided an added support in showing that hetero-oligomerization was energetically favorable. The hetero-oligomeric populations of PKM2 showed altered activity and affinity, and their expression resulted in an increased growth charge per unit of Escherichia coli as well as mammalian cells, forth with an increased rate of polyploidy. These features are known to be essential to tumor progression.[8]
Potential multi-functional protein [edit]
[nine]
See too [edit]
- glycolysis
- tumor metabolome
- PKM2
References [edit]
- ^ Haug, U.; Rothenbacher, D.; Wente, Yard. North.; Seiler, C. One thousand.; Stegmaier, C.; Brenner, H. (2007). "Tumour M2-PK equally a stool marking for colorectal cancer: Comparative analysis in a big sample of unselected older adults vs colorectal cancer patients". British Journal of Cancer. 96 (9): 1329–34. doi:x.1038/sj.bjc.6603712. PMC2360192. PMID 17406361.
- ^ 4004.pdf Archived 2014-x-09 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Tumor M2-PK Stool Exam". Retrieved June eight, 2013.
- ^ Oremek, M; Kukshaĭte, R; Sapoutzis, N; Ziolkovski, P (2007). "The significance of TU M2-PK tumor mark for lung cancer diagnostics". Klinicheskaia Meditsina. 85 (7): 56–58. PMID 17882813.
- ^ Roigas J, Schulze Thousand, Raytarowski S, Jung Grand, Schnorr D, Loening SA. (September 2001). "Tumor M2 pyruvate kinase in plasma of patients with urological tumors". Neoplasm Biol. 22 (v): 282–five. doi:10.1159/000050628. PMID 11553857. S2CID 46855687.
{{cite periodical}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bluemlein K, Grüning NM, Feichtinger RG, Lehrach H, Kofler B, Ralser M (2011). "No evidence for a shift in pyruvate kinase PKM1 to PKM2 expression during tumorigenesis". Oncotarget. two (5): 393–400. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.278. PMC3248187. PMID 21789790.
- ^ Akhtar Chiliad, Gupta Five, Koul A, Alam Due north, Bhat R, Bamezai RN (May 2009). "Differential behavior of missense mutations in the intersubunit contact domain of the human pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme". J. Biol. Chem. 284 (18): 11971–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808761200. PMC2673266. PMID 19265196.
- ^ Gupta V, Kalaiarasan P, Faheem M, Singh North, Iqbal MA, Bamezai RN (May 2010). "Dominant negative mutations affect oligomerization of human pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme and promote cellular growth and polyploidy". J. Biol. Chem. 285 (22): 16864–73. doi:ten.1074/jbc.M109.065029. PMC2878009. PMID 20304929.
- ^ Gupta V, Bamezai RN (Sep 2010). "Human pyruvate kinase-M2: "A multi-functional poly peptide"". Protein Sci. nineteen (11): 2031–44. doi:10.1002/pro.505. PMC3005776. PMID 20857498.
Stool [edit]
- Hardt PD, Mazurek South, Toepler M, Schlierbach P, Bretzel RG, Eigenbrodt Due east, Kloer HU (2004). "Faecal neoplasm M2 pyruvate kinase: a new, sensitive screening tool for colorectal cancer. Brit. J". Cancer. 91 (v): 980–984. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602033. PMC2409989. PMID 15266315.
- Koss Thousand, Maxton D, Jankowski JAZ. The potential use of fecal dimeric M2 pyruvate kinase (Tumor M2-PK) in screening for colorectal cancer (CRC). Abstruse from Digestive Disease Week, May 2005; Chicago, Usa.
- Mc Loughlin R, Shiel Eastward, Sebastian Due south, Ryan B, O´Connor HJ, O´Morain C. Tumor M2-PK, a novel screening tool for colorectal cancer. Abstract from Digestive Affliction Week, May 2005, Chicago/Us
Plasma [edit]
- Cerwenka H, Aigner R, Bacher H, Werkgartner G, El-Shabrawi A, Quehenberger F, Mischinger HJ (1999). "TUM2-PK (pyruvate kinase type tumor M2), CA19-9 and CEA in patients with benign, malignant and metastasizing pancreatic lesions". Anticancer Res. xix (1B): 849–52. PMID 10216504.
- Kaura B, Bagga R, Patel FD (2004). "Evaluation of the pyruvate kinase isoenzyme tumor (Tu M2-PK) as a tumor marking for cervical carcinoma". J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 30 (iii): 193–196. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0756.2004.00187.x. PMID 15210041. S2CID 31214841.
- Kim CW, Kim JI, Park SH, et al. (November 2003). "Usefulness of plasma tumor M2-pyruvate kinase in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer". The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology = Taehan Sohwagi Hakhoe Chi. 42 (5): 387–93. PMID 14646575.
- Lüftner D, Mesterharm J, Akrivakis C, Geppert R, Petrides PE, Wernecke KD, Possinger K (2000). "Tumor M2-pyruvate kinase expression in advanced breast cancer". Anticancer Res. twenty (6D): 5077–5082. PMID 11326672.
- Oremek GM, Teigelkamp Southward, Kramer W, Eigenbrodt E, Usadel KH (1999). "The pyruvate kinase isoenzyme tumor M2 (Tu M2-PK) as a tumor mark for renal carcinoma". Anticancer Res. 19 (4A): 2599–2601. PMID 10470201.
- Schneider J, Morr H, Velcovsky HG, Weisse G, Eigenbrodt Due east (2000). "Quantitative detection of tumor M2-pyruvate kinase in plasma of patients with lung cancer in comparison to other lung diseases". Cancer Detection and Prevention. 24 (6): 531–5. PMID 11198266.
- Schneider J, Schulze Grand (2003). "Comparing of Tumor M2-pyruvate kinase (Tumor M2-PK), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), sugar antigens CA 19-9 and CA 724 in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer". Anticancer Res. 23 (6D): 5089–5095. PMID 14981971.
- Ugurel S, Bell Northward, Sucker A, Zimpfer A, Rittgen W, Schadendorf D (2005). "Tumor type M2 pyruvate kinase (TuM2-PK) equally a novel plasma tumor marking in melanoma". Int. J. Cancer. 117 (5): 825–830. doi:10.1002/ijc.21073. PMID 15957165.
- Ventrucci M, Cipolla A, Racchini C, Casadei R, Simoni P, Gullo L (2004). "Tumor M2-pyruvate kinase, a new metabolic marker for pancreatic cancer". Dig. Dis. Sci. 49 (7–8): 1149–1155. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000037803.32013.aa. PMID 15387337. S2CID 1237419.
- Wechsel HW, Petri E, Bichler KH, Feil G (1999). "Marker for renal carcinoma (RCC): The dimeric grade of pyruvate kinase type M2 (Tu M2-PK)". Anticancer Res. nineteen (4A): 2583–2590. PMID 10470199.
- Zhang B, Chen JY, Chen DD, Wang GB, Shen P (2004). "Tumor type M2 pyruvate kinase expression in gastric cancer, colorectal cancer and controls". World J. Gastroenterol. 10 (eleven): 1643–1646. doi:10.3748/wjg.v10.i11.1643. PMC4572770. PMID 15162541.
Scientific background [edit]
- Mazurek Southward, Boschek CB, Hugo F, Eigenbrodt Due east (2005). "Pyruvate kinase type M2 and its role in tumor growth and spreading". Semin. Cancer Biol. fifteen (4): 300–308. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.04.009. PMID 15908230.
External links [edit]
- Tumor M2-PK as a diagnostic biomarker
- The pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2
Michaelis Menten Vs Lineweaver Burk,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_M2-PK
Posted by: jonesdescuseence.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Michaelis Menten Vs Lineweaver Burk"
Post a Comment